고정 헤더 영역
상세 컨텐츠
본문 제목
DistilBERT, a distilled version of BERT: smaller, faster, cheaper and lighter 논문 리뷰
본문

DistilBERT, a distilled version of BERT: smaller, faster, cheaper and lighter 논문 리뷰
Google Machine Learning Bootcamp 2022 에서 "NLP 논문 리뷰 스터디" 에 참여하며 정리한 자료입니다
Abstract

- DistilBERT (smaller, faster, lighter) : 더 작은 크기의 일반화된 language model (여러 NLP task에 적용가능한)
- pre-training 에서의 knowledge distilation 수행
- BERT의 40% 크기
- Language Understanding 측면에서 97%의 성능 유지
- 학습속도 60% 향상
- Triple loss 사용
- language modeling
- distillation
- cosine-distance loss
1. Introduction
최근 연구에서 large-scale pre-trained language model + Fine-tuning 사용하는 것이 Trend이다.
그러나, 모델 크기 증가에 수반되는 문제점으로
- environmental cost
- on-device 실시간 추론이 어렵다 : 모델연산 및 메모리 요구량 증가
따라서, knowledge distillation 을 통해 빠른 추론시간과, 여러 downstream task에서 여전히 잘 작동하는 작은 language model 인 DistilBERT를 제안한다.
DistilBERT는 triple loss를 사용하여, 거의 동일한 성능에, 40% 작은 크기와 60% 빠른 추론시간을 가진 모델이다.
2. Knowledge distillation
Knowledge distillation
student 모델이 대용량 크기의 teacher 모델을 모방하려 학습하는 일종의 compression 방법이다
잘 학습된 teach 모델의 경우, 학습데이터에 대해 정답에 높은 확률이 부여되고, 정답이 아닌 label에는 0에 가까운 확률이 부여된 output distribution 을 예측한다
그런데, 학습데이터에 대해 정답이 아닌 label 확률이 완전히 0에 가깝지 않은 경우, 이는 비교적 낮은 정도의 overfitting 을 뜻하므로, 이 경우 generalization 성능이 더 높다고 이해할 수 있다.
Training loss
- distillation loss : teacher 모델의 soft target probability 와의 loss 계산
- distillation loss 에서의 ti 는 label 에 대한 teacher model 의 probability
- 확률 ti 계산 시, smoothness (확률 간 차이 정도) 를 결정하는 softmax temperature (T)를 사용
- 학습 시에 student, teacher 모델 모두 T를 사용하고, 추론 시에는 T를 1로 고정
- MLM loss 에서의 ti 는 MLM에서의 정답 token
- cosine-embedding loss : student 모델과 teacher 모델의 hidden state 간 차이
- Final loss : linear combination of MLM loss and distillation loss + cosine-embedding loss


3. DistilBERT : a distilled version of BERT
Student architecture
- token type embedding, pooler 제거
- layer 수는 2의 거듭제곱으로 감소 (hidden size 보다 연산 효율성에 더 큰 영향)
Student initialization
- 초기화에 Teacher 모델 layer 의 2개 당 한개 layer 사용 (dim 동일)
Distillation
- gradient accumulation(up to 4K per batch) + dynamic masking + no NSP
Data and compute power
- BERT와 동일 : English Wiki + BookCorpus (16GB)
4. Experiments
General Language Understanding
- DistilBERT의 GLUE 밴치마크 성능 측정
- ensembling이나 multi-task learning 사용X
- ELMo, BERT와 비교 : ELMo 보다 높은 성능, BERT보다 40% 더 적은 파라미터 및 97%의 성능
4.1 Downstream task benchmark
Downstream tasks
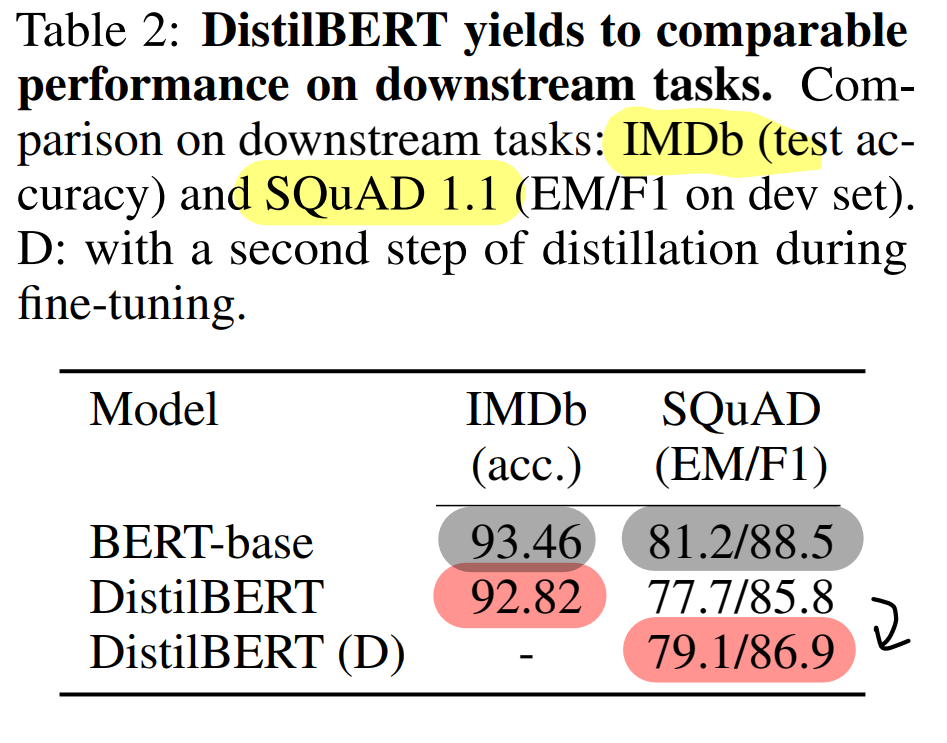
- classification(IMDb sentiment classification), QA (SQuAD v1.1)
- DistilBERT: BERT보다 40% 작은 크기
- IMDb 에서 단 0.6% 차이
- SQuAD 에서 단 3.9% 차이
- Pre-train(Distillation) + Fine-tuning(Distillation) 시도 : 성능 추가 증가

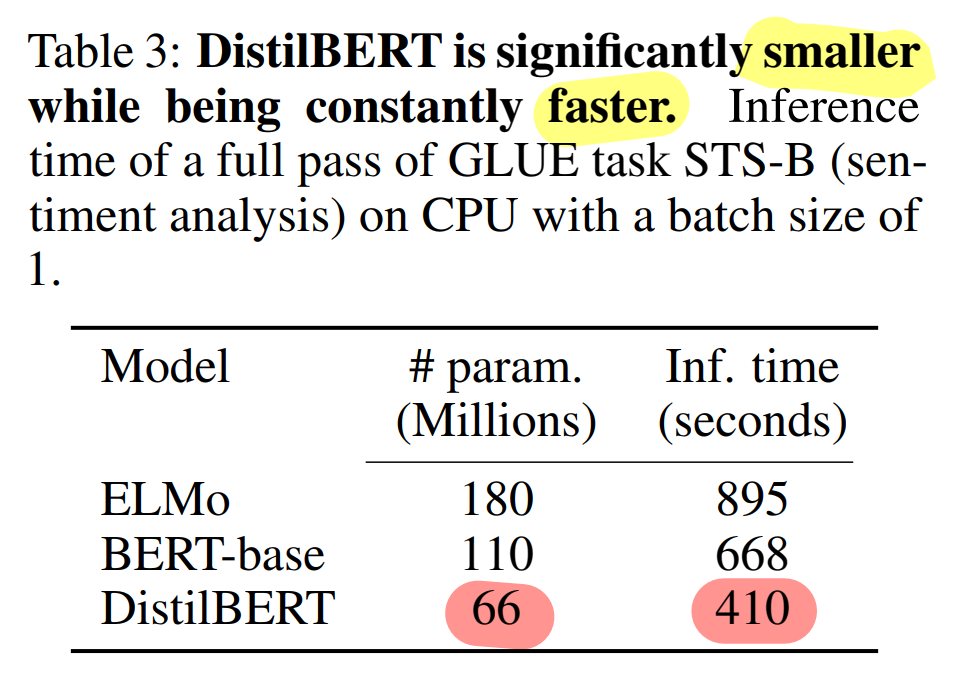
Size and inference speed
DistilBERT는 BERT의 40% 적은 파라미터, 60% 빠른 추론 속도 (STS-B 기준)
On device computation
- distilBERT vs BERT+QA : iPhone 7 Plus
- BERT대비 71% 빠른 추론 속도 (tokenization 제외)
- 207MB의 light weight
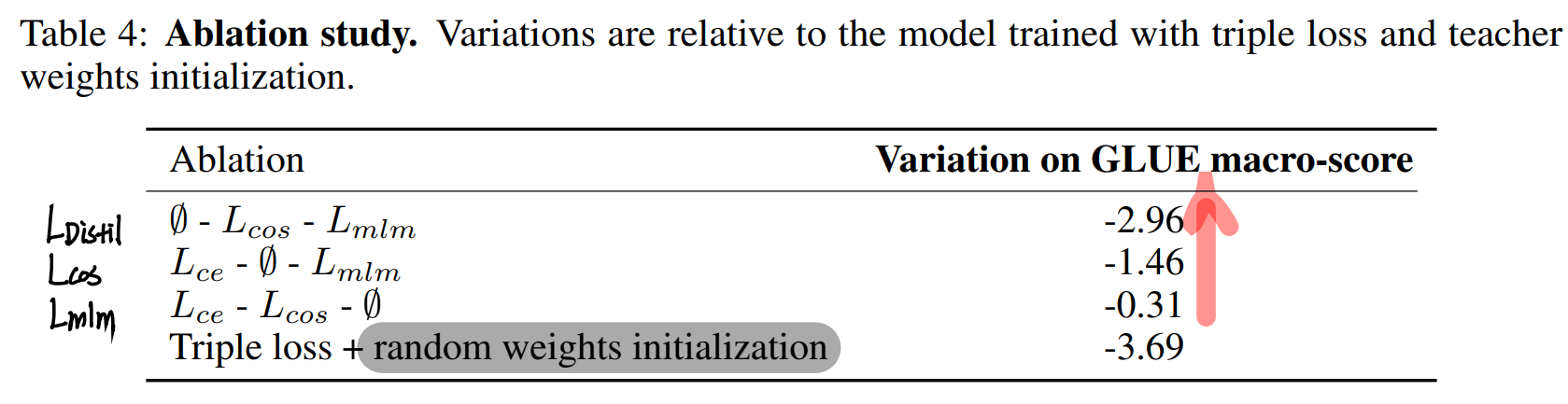
4.2 Ablation study
triple loss 구성을 하나씩 제외하며 성능 변화 측정
- Distillation Loss, Cosine-embedding loss, MLM loss 순으로 큰 성능 drop 확인
- Distillation Loss 이 성능 견인에 가장 큰 영향
- student initialization 도 큰 영향 (random init 시 큰 성능 drop)
5. Related work
Task-specific distillation
- BERT → LSTM (classification)
- BERT+SQuAD → small transformer + init from BERT
- DistilBERT: Pre-training 에서의 Knowledge Distilation
Multi-distillation
- ensemble of teachers (multi-task learning)
- Large QA models → QA model
- multi models → multilingual model
- DistilBERT: distillation + MLM + cosine loss
Other compression techniques
- weight pruning : 추론 시 attention head 제거(min = 1)
- Quantization
6. Conclusion and future work
- DistilBERT : 40% smaller, 60% faster, 97% 성능
- Pre-training에서의 distillation을 통해 효율적이고 general 한 language model 을 학습
DistilBERT Code Implementation
from transformers.models.roberta.modeling_roberta import RobertaPreTrainedModel, RobertaConfig
def distill_roberta(
teacher_model : RobertaPreTrainedModel,
) -> RobertaPreTrainedModel:
"""
Distilates a RoBERTa (teacher_model) like would DistilBERT for a BERT model.
The student model has the same configuration, except for the number of hidden layers, which is // by 2.
The student layers are initilized by copying one out of two layers of the teacher, starting with layer 0.
The head of the teacher is also copied.
"""
# Get teacher configuration as a dictionnary
configuration = teacher_model.config.to_dict()
# Half the number of hidden layer : 2의 거듭제곱으로 layer 감소 (factor of 2)
configuration['num_hidden_layers'] //= 2
# Convert the dictionnary to the student configuration
configuration = RobertaConfig.from_dict(configuration)
# Create uninitialized student model : student model 정의
student_model = type(teacher_model)(configuration)
# Initialize the student's weights : teacher model weight로 student model 초기화
distill_roberta_weights(teacher=teacher_model, student=student_model)
# Return the student model
return student_modelfrom transformers.models.roberta.modeling_roberta import RobertaEncoder, RobertaModel
from torch.nn import Module
# 계층에 따라 재귀적으로 layer 가중치 초기화 실행 (roberta layer 구조 이미지 참고)
def distill_roberta_weights(
teacher : Module,
student : Module,
) -> None:
"""
Recursively copies the weights of the (teacher) to the (student).
This function is meant to be first called on a RobertaFor... model, but is then called on every children of that model recursively.
The only part that's not fully copied is the encoder, of which only half is copied.
"""
# If the part is an entire RoBERTa model or a RobertaFor..., unpack and iterate
if isinstance(teacher, RobertaModel) or type(teacher).__name__.startswith('RobertaFor'):
for teacher_part, student_part in zip(teacher.children(), student.children()):
distill_roberta_weights(teacher_part, student_part)
# Else if the part is an encoder, copy one out of every layer : encoder의 2개 layer 당 1개씩만 초기화에 활용
elif isinstance(teacher, RobertaEncoder):
teacher_encoding_layers = [layer for layer in next(teacher.children())]
student_encoding_layers = [layer for layer in next(student.children())]
for i in range(len(student_encoding_layers)):
student_encoding_layers[i].load_state_dict(teacher_encoding_layers[2*i].state_dict())
# Else the part is a head or something else, copy the state_dict
else:
student.load_state_dict(teacher.state_dict())
from torch import Tensor
def get_logits(
model : RobertaPreTrainedModel,
input_ids : Tensor,
attention_mask : Tensor,
) -> Tensor:
"""
Given a RoBERTa (model) for classification and the couple of (input_ids) and (attention_mask),
returns the logits corresponding to the prediction.
"""
return model.classifier(
model.roberta(input_ids, attention_mask)[0]
)import torch
from torch.nn import CrossEntropyLoss, CosineEmbeddingLoss
# DiltilBERT의 Final Loss : Distil Loss + MLM Loss (supervised taks) + Cosine-embdding Loss
def distillation_loss(
teacher_logits : Tensor,
student_logits : Tensor,
labels : Tensor,
temperature : float = 1.0,
) -> Tensor:
"""
The distillation loss for distilating a BERT-like model.
The loss takes the (teacher_logits), (student_logits) and (labels) for various losses.
The (temperature) can be given, otherwise it's set to 1 by default.
"""
# Temperature and sotfmax
student_logits, teacher_logits = (student_logits / temperature).softmax(1), (teacher_logits / temperature).softmax(1)
# Classification loss (problem-specific loss) : MLM 또는 supervised task의 loss
loss = CrossEntropyLoss()(student_logits, labels)
# CrossEntropy teacher-student loss : teacher과 student 모델의 soft label 간 loss
loss = loss + CrossEntropyLoss()(student_logits, teacher_logits)
# Cosine loss : teacher, student 모델 간 hidden state의 유사도 loss
loss = loss + CosineEmbeddingLoss()(teacher_logits, student_logits, torch.ones(teacher_logits.size()[0]))
# Average the loss and return it
loss = loss / 3
return loss
스터디원들과의 QnA 및 Discussion
Temperature (T) 사용의 의미 : T 증가 시, label 간 확률 편차가 감소한다 (= Entropy가 증가한다, 정보량이 많다)
Q. 제프리 힌튼의 DistilBERT 에 앞서, Distillation을 소개한 "Distilling the Knowledge in a Neural Network" 논문의 Loss 함수 내 상수 alpha 의 영향은?

α가 감소함에 따라 distilation 의 영향은 줄어들고, supervised task 에 대한 loss 의 영향이 커진다. 반대로 증가시킨다면, Total loss 에 대한 distillation loss 의 영향력을 높이는 것과 같다
Q. Large Batch 가 유리한 이유?
A. 최적화 과정에 사용되는 맥락 정보가 smaller batch보다 더 많기 때문이다!
Q. DistilBERT의 paper 길이가 역대급으로 짧은 이유는..?
A. Teacher paper ("Distilling the Knowledge in a Neural Network") 에서 Student paper(DistilBERT)로 paper마저 증류해버린 Jefferey Hinton, the distillator...
<Reference>
Sanh, V., Debut, L., Chaumond, J., & Wolf, T. (2019). DistilBERT, a distilled version of BERT: smaller, faster, cheaper and lighter. arXiv preprint arXiv:1910.01108
https://developpaper.com/code-implementation-of-distillation-class-bert-model-using-distilbert/





댓글 영역